Optical Coherence Tomography
a promising diagnostic approach for coronary artery blockade and PCI (stent)
What is OCT?
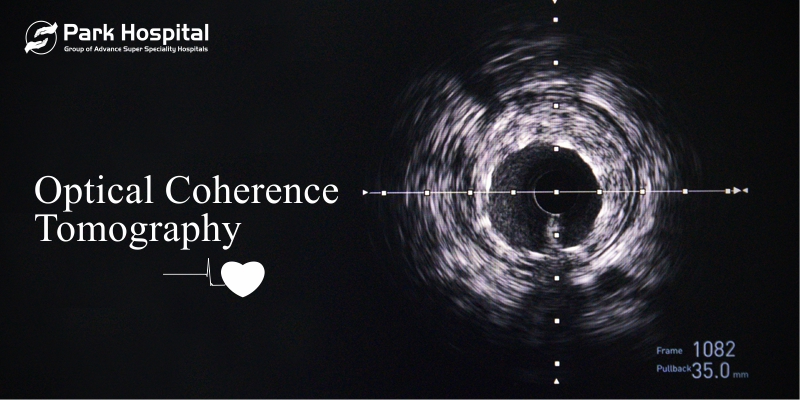
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), is an imaging technique developed in 1990 and first used in 1991 to produce images of blood vessels, especially the coronary arteries.
How is OCT different from IVUS?
Unlike Intra Vascular Ultra Sound (IVUS) examination, OCT uses near-infrared light to provide cardiologists to see inside an artery with 10 times higher resolution and clarity than IVUS and cross five out of 6 tight lesions that were otherwise unable to be crossed by IVUS catheter.
Are there no disadvantages with first-generation OCT?
The disadvantage of first-generation time-domain OCT (TD-OCT) was it was a more complex procedure than IVUS and employs a mechanical scanning process that limits the rate of images.
How did OCT evolve?
The next-generation OCT systems are called frequency domain OCTs (FD-OCT) that employ a tunable laser light source with a range of infrared light (1250-1370 nm) rather than a fixed wavelength of first-generation OCT. Hence, the advantage of faster image acquisition rates, pullback speeds, and simpler non-occlusive approach.
How does OCT help cardiologists in placing coronary interventions (stents)?
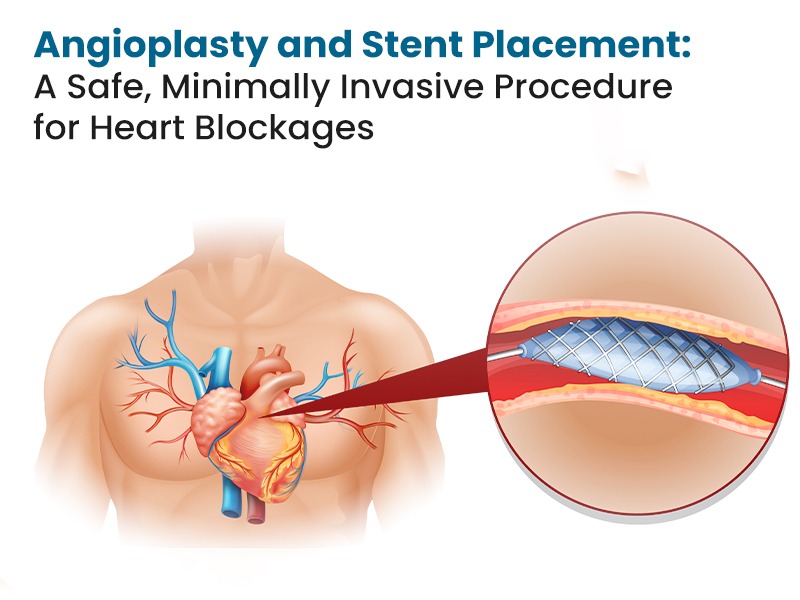
OCT is used with angioplasty by Cardiologists to unblock a coronary artery. OCT helps a cardiologist to have clarity on how much fat or clot is in the artery and is safe to guide stent placement against the artery wall. OCT is especially useful in distal left main coronary artery disease due to high resolution and in blood vessels less than 5mm in diameter. More than 90% of quadrants of LM (left main) are assessable with a distinct ability to detect 60% more atherosclerotic plaques (blocks) than angiography. OCT is especially useful in guiding stents in the Left Main Coronary artery.
Advantages of OCT during and post-stent placement
OCT-guided stent placement had a significantly lower non-fatal MI or 1-year composite of cardiac death. Post-stenting OCT assessment revealed suboptimal stent implantation (an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events) in almost 31% of angiography-guided stent placement cases during follow-up. Specifically, OCT also revealed other predictors of MACE such as in-stent minimal luminal area of <4.5mm2 in 23% of stented lesions, plaque formation within stent after placement in 29% of cases, and narrowing of blood vessel lumen in 7.5% of cases.
OCT can evaluate the lipid pool clearly by estimating the length of the lipid pool in blood vessels, which may predict ST resolution after primary PCI.
Conclusion
Overall, Optical Coherence Tomography is a reliable tool for cardiologists that has comprehensive applications, not just in the assessment of coronary artery blockage and the number of lesions but also to guide stent placement and also to reveal post-stenting complications.
Park Hospital is the best heart hospital. With the most advanced technologies and highly experienced cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, they provide comprehensive cardiac treatment.