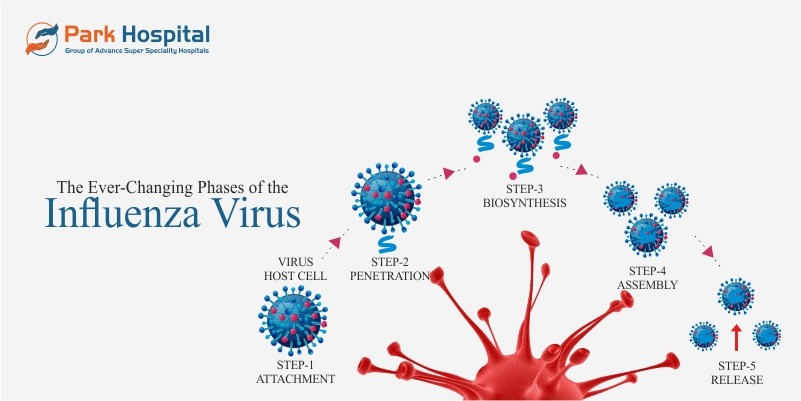
What is a nosebleed?
Nose bleed (Epistaxis) is obviously known to be a loss of blood from tissue that lines inside of your nose. Nose bleeds are as common as 60% of people have nose bleeds at least once in their lifetime. Most nose bleeds are not serious and could be managed at home.
What are the kinds of nosebleeds?
There are two different kinds of nose bleeds based on the site of bleeding - anterior nose bleeding which is not serious and most common in children, and posterior nose bleeding which occurs in the back part of the nose near the throat seen in adults and is more complicated as it may result in heavy bleeding. Nose bleeds may be seen in –
In children (5-10 years of age) due to dry air, colds, and allergies.
Adults (45-75 years of age) due to intake of blood thinning drugs, high B.P., or nose pricking.
Pregnant women due to the expansion of blood vessels, thinning of the lumen that is vulnerable to more blood pressure on such delicate blood vessels.
In people with clotting disorders such as hemophilia, experience continuous loss of blood.
What are the common causes of nose bleeds?
Nose pricking
Upper respiratory tract infections and sinusitis
Repeated episodes of sneezing and nose blowing
Injury to the nose
Allergic rhinitis (running nose), Nual POLYPOSIS
Chemical irritants (exposure to chemicals at industrial workplaces).
Apart from the above common causes, bleeding may also be due to alcohol use, leukemia, nasal polyps, nasal tumors, high B.P., or due to facial or nasal surgery.
How can you stop a nosebleed at home?
Follow these six steps to stop common nose bleeds at home –
Relax, Sit upright and lean slightly forward to prevent any blood from running down your throat and prevent nausea or vomiting.
Breathe through your mouth
Stop the blood through tissue or a damp hygienic cloth.
Use your thumb and index finger to pinch together the soft exterior part of your nose for at least 5 minutes. In case it is still bleeding, squeeze the nose for 10 minutes & apply ice pack.
After the bleeding stops, do not bend over, strain or lift anything heavy.
Do not strain your nose by rubbing or blowing immediately.
When should you see a doctor for these nose bleeds?
Visit an ENT Specialist in case of the following scenarios –
Bleeding could not be stopped after squeezing the nose for more than 15-20 minutes.
Rapid and large blood loss
Blood vomiting due to swallowing
Nose bleed followed by head injury (due to fall)
Frequent nose bleeds
Symptoms of anemia are seen such as fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin, etc.
Nose bleeding in children under 2 years of age.
While using blood thinning drugs, or having blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia.
How are nose bleeds treated?
Nose bleeds are treated based on their cause. Some of the treatments are –
Nasal packing – Insertion of gauze or MEROCEL Nasal pack into the nose for 24-48 hours to create pressure at the site of bleeding.
Medications such as Tranexamic acid helps blood clotting
Cauterization – involves chemical treatment (silver nitrate) to seal the ruptured blood vessel under the influence of a local anesthetic.
In the case of a fractured nose or a deviated septum, a surgical repair is an option.
Ligation – the bleeding vessel is tied off.
Nose bleeds are most common and less serious in children but are considered serious in case of adults where the underlying cause is mostly due to disorder.
If you are suffering from Nose Bleeding, consult our ENT Specialists for accurate diagnosis and treatment, at Park Hospital, Gurgaon.
In children (5-10 years of age) due to dry air, colds, and allergies.
Adults (45-75 years of age) due to intake of blood thinning drugs, high B.P., or nose pricking.
Pregnant women due to the expansion of blood vessels, thinning of the lumen that is vulnerable to more blood pressure on such delicate blood vessels.
In people with clotting disorders such as hemophilia, experience continuous loss of blood.
Nose pricking
Upper respiratory tract infections and sinusitis
Repeated episodes of sneezing and nose blowing
Injury to the nose
Allergic rhinitis (running nose), Nual POLYPOSIS
Chemical irritants (exposure to chemicals at industrial workplaces).
Relax, Sit upright and lean slightly forward to prevent any blood from running down your throat and prevent nausea or vomiting.
Breathe through your mouth
Stop the blood through tissue or a damp hygienic cloth.
Use your thumb and index finger to pinch together the soft exterior part of your nose for at least 5 minutes. In case it is still bleeding, squeeze the nose for 10 minutes & apply ice pack.
After the bleeding stops, do not bend over, strain or lift anything heavy.
Do not strain your nose by rubbing or blowing immediately.
Bleeding could not be stopped after squeezing the nose for more than 15-20 minutes.
Rapid and large blood loss
Blood vomiting due to swallowing
Nose bleed followed by head injury (due to fall)
Frequent nose bleeds
Symptoms of anemia are seen such as fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin, etc.
Nose bleeding in children under 2 years of age.
While using blood thinning drugs, or having blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia.
Nasal packing – Insertion of gauze or MEROCEL Nasal pack into the nose for 24-48 hours to create pressure at the site of bleeding.
Medications such as Tranexamic acid helps blood clotting
Cauterization – involves chemical treatment (silver nitrate) to seal the ruptured blood vessel under the influence of a local anesthetic.
In the case of a fractured nose or a deviated septum, a surgical repair is an option.
Ligation – the bleeding vessel is tied off.